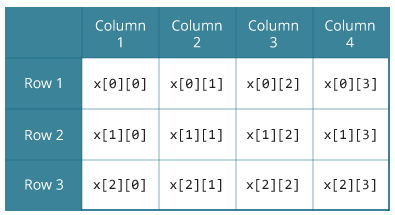
Here, x is a two-dimensional (2d) array. The array can hold 12 elements. You can think the array as a table with 3 rows and each row has 4 columns.

Similarly, you can declare a three-dimensional (3d) array. For example,
float y[2][4][3];Here, the array y can hold 24 elements.
Here is how you can initialize two-dimensional and three-dimensional arrays:
// Different ways to initialize two-dimensional array int c[2][3] = , >; int c[][3] = , >; int c[2][3] = ; You can initialize a three-dimensional array in a similar way to a two-dimensional array. Here's an example,
int test[2][3][4] = < , , >, , , >>;// C program to store temperature of two cities of a week and display it. #include const int CITY = 2; const int WEEK = 7; int main() < int temperature[CITY][WEEK]; // Using nested loop to store values in a 2d array for (int i = 0; i < CITY; ++i) < for (int j = 0; j < WEEK; ++j) < printf("City %d, Day %d: ", i + 1, j + 1); scanf("%d", &temperature[i][j]); >> printf("\nDisplaying values: \n\n"); // Using nested loop to display vlues of a 2d array for (int i = 0; i < CITY; ++i) < for (int j = 0; j < WEEK; ++j) < printf("City %d, Day %d = %d\n", i + 1, j + 1, temperature[i][j]); >> return 0; > Output
City 1, Day 1: 33 City 1, Day 2: 34 City 1, Day 3: 35 City 1, Day 4: 33 City 1, Day 5: 32 City 1, Day 6: 31 City 1, Day 7: 30 City 2, Day 1: 23 City 2, Day 2: 22 City 2, Day 3: 21 City 2, Day 4: 24 City 2, Day 5: 22 City 2, Day 6: 25 City 2, Day 7: 26 Displaying values: City 1, Day 1 = 33 City 1, Day 2 = 34 City 1, Day 3 = 35 City 1, Day 4 = 33 City 1, Day 5 = 32 City 1, Day 6 = 31 City 1, Day 7 = 30 City 2, Day 1 = 23 City 2, Day 2 = 22 City 2, Day 3 = 21 City 2, Day 4 = 24 City 2, Day 5 = 22 City 2, Day 6 = 25 City 2, Day 7 = 26
// C program to find the sum of two matrices of order 2*2 #include int main() < float a[2][2], b[2][2], result[2][2]; // Taking input using nested for loop printf("Enter elements of 1st matrix\n"); for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) < printf("Enter a%d%d: ", i + 1, j + 1); scanf("%f", &a[i][j]); >// Taking input using nested for loop printf("Enter elements of 2nd matrix\n"); for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) < printf("Enter b%d%d: ", i + 1, j + 1); scanf("%f", &b[i][j]); >// adding corresponding elements of two arrays for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) < result[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j]; >// Displaying the sum printf("\nSum Of Matrix:"); for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) < printf("%.1f\t", result[i][j]); if (j == 1) printf("\n"); >return 0; >Output
Enter elements of 1st matrix Enter a11: 2; Enter a12: 0.5; Enter a21: -1.1; Enter a22: 2; Enter elements of 2nd matrix Enter b11: 0.2; Enter b12: 0; Enter b21: 0.23; Enter b22: 23; Sum Of Matrix: 2.2 0.5 -0.9 25.0
// C Program to store and print 12 values entered by the user #include int main() < int test[2][3][2]; printf("Enter 12 values: \n"); for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) < for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j) < for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) < scanf("%d", &test[i][j][k]); >> > // Printing values with the proper index. printf("\nDisplaying values:\n"); for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) < for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j) < for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) < printf("test[%d][%d][%d] = %d\n", i, j, k, test[i][j][k]); >> > return 0; >Output
Enter 12 values: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Displaying Values: test[0][0][0] = 1 test[0][0][1] = 2 test[0][1][0] = 3 test[0][1][1] = 4 test[0][2][0] = 5 test[0][2][1] = 6 test[1][0][0] = 7 test[1][0][1] = 8 test[1][1][0] = 9 test[1][1][1] = 10 test[1][2][0] = 11 test[1][2][1] = 12